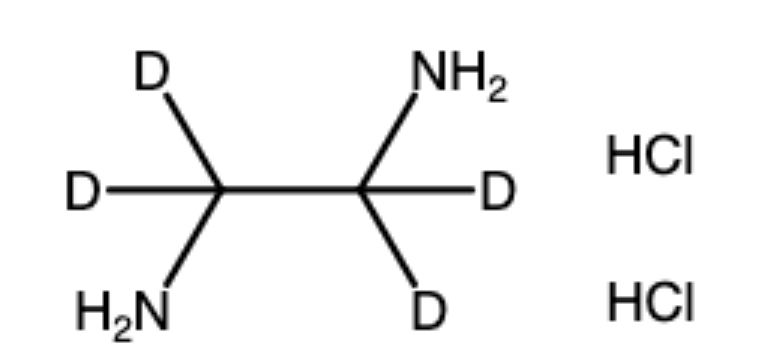
Ethylene Diamine Dihrdrochloride-d4
Category
Sub-Category
Completed orders
Price
Delivery Cost
Minimum Order
Location
DESCRIPTION:
Ethylenediamine-1,1,2,2-D4 Dihydrochloride is a high-purity, deuterium-labeled compound widely used in analytical chemistry, pharmaceutical research, and isotopic studies. This compound is the deuterated form of ethylenediamine dihydrochloride, where all four hydrogens on the ethylenediamine backbone are replaced by deuterium (D).
Researchers choose Ethylenediamine-1,1,2,2-D4 Dihydrochloride for its superior performance as an internal standard in mass spectrometry (MS) and as a stable isotope tracer in metabolic and pharmacokinetic studies.
Key Features of Ethylenediamine-1,1,2,2-D4 Dihydrochloride:
-
Chemical Name: Ethylenediamine-1,1,2,2-D4 Dihydrochloride
-
Synonyms: EDA-d4·2HCl, [²H₄]-ethane-1,2-diamine dihydrochloride
-
Molecular Formula: C₂H₄D₄N₂·2HCl
-
Molecular Weight: ~132.1 g/mol
-
Isotopic Labeling: Deuterium substitution at all four hydrogens
Chemical Name: Ethylenediamine-1,1,2,2-D4 Dihydrochloride
Synonyms: EDA-d4·2HCl, [²H₄]-ethane-1,2-diamine dihydrochloride
Molecular Formula: C₂H₄D₄N₂·2HCl
Molecular Weight: ~132.1 g/mol
Isotopic Labeling: Deuterium substitution at all four hydrogens
Applications of Ethylenediamine-1,1,2,2-D4 Dihydrochloride:
Ethylenediamine-1,1,2,2-D4 Dihydrochloride is essential for:
-
Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS, GC-MS):
Acts as an internal standard for precise quantification. -
NMR Spectroscopy:
Deuterium substitution minimizes background interference. -
Metabolomics & Tracer Studies:
Tracks amine pathways and biological transformations. -
Pharmaceutical & Drug Research:
Used in drug metabolism, stability, and bioavailability studies.
Physical & Chemical Properties of Ethylenediamine-1,1,2,2-D4 Dihydrochloride:
-
Appearance: White crystalline powder
-
Solubility: Soluble in water and ethanol
-
Stability: Stable under normal laboratory conditions; hygroscopic
-
Storage: Store at 2–8 °C, dry and protected from light
Appearance: White crystalline powder
Solubility: Soluble in water and ethanol
Stability: Stable under normal laboratory conditions; hygroscopic
Storage: Store at 2–8 °C, dry and protected from light
Safety & Handling of Ethylenediamine-1,1,2,2-D4 Dihydrochloride:
Like most laboratory chemicals, Ethylenediamine-1,1,2,2-D4 Dihydrochloride should be handled with care:
-
Hazards: May cause skin, eye, or respiratory irritation
-
Precautions: Use gloves, goggles, and protective clothing
-
Disposal: Follow standard laboratory chemical waste protocols
Why Choose Ethylenediamine-1,1,2,2-D4 Dihydrochloride?
Ethylenediamine-1,1,2,2-D4 Dihydrochloride is trusted by researchers worldwide due to its:
-
High isotopic purity
-
Consistent quality for reproducible results
-
Compatibility with advanced analytical instruments
-
Essential role in isotope labeling and tracer studies

Overall Rating
Description Rating
Delivery time
Contact
Professionalism
You may like this

Insulin Glargine Metabolite M2
![Insulin Glargine Metabolite M1-[13C6 15N Leu]4](https://pub-5c3fc080af7d4ef9baded3d096e6f3db.r2.dev/uploads/product/full/1766753148_TPC41119.png)
Insulin Glargine Metabolite M1-[13C6 15N Leu]4
![Insulin Glargine Metabolite M2-[13C6 15N Leu]4](https://pub-5c3fc080af7d4ef9baded3d096e6f3db.r2.dev/uploads/product/full/1766752981_TPC41121.png)
Insulin Glargine Metabolite M2-[13C6 15N Leu]4